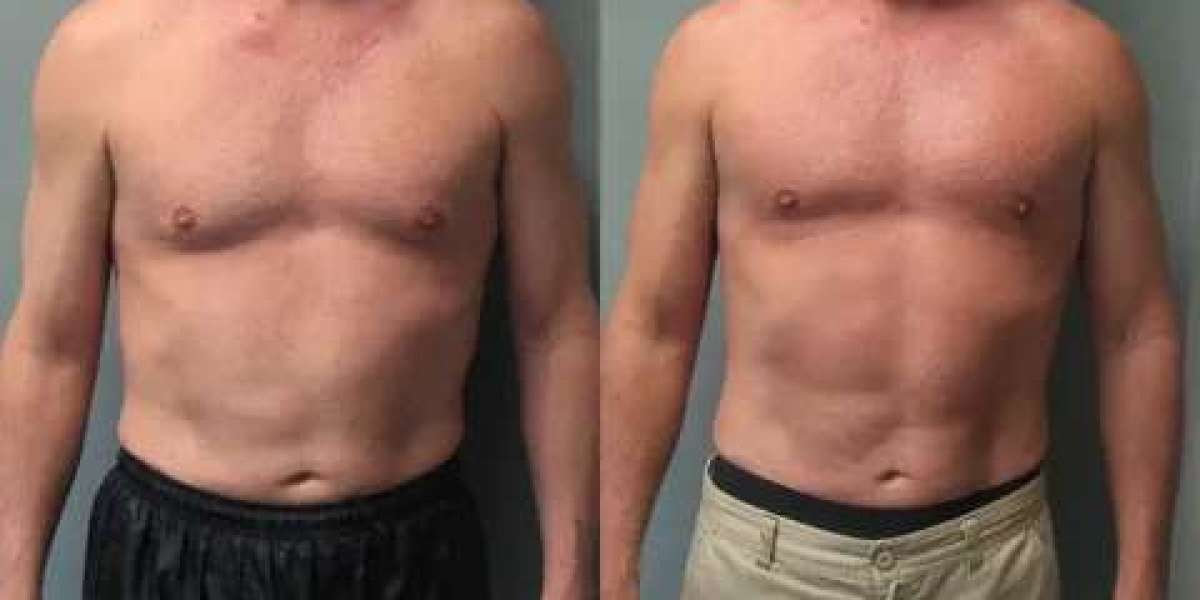
Gynecomastia, the enlargement of male breast tissue, is a common condition that can affect men of all ages. While it is often harmless, it can cause physical discomfort, emotional stress, and self-consciousness. Knowing when to seek medical advice is essential for effective treatment and long-term results.
Some cases of gynecomastia resolve on their own, particularly during adolescence. However, persistent, painful, or rapidly worsening symptoms may indicate the need for professional evaluation. Early consultation can help determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment, whether medical or surgical.
For expert evaluation and access to the latest treatment options, patients can consult Gynecomastia in Islamabad for personalized care and professional guidance.
Signs That Require Medical Attention
While mild gynecomastia may not require intervention, certain symptoms suggest that a medical consultation is necessary:
Persistent Breast Enlargement: Enlargement lasting more than six months in adolescents or adults.
Pain or Tenderness: Continuous discomfort or pain around the breast tissue.
Rapid Growth: Sudden increase in breast size over weeks or months.
Asymmetry: Noticeable differences between the two sides of the chest.
Nipple Discharge: Any fluid leaking from the nipple warrants immediate attention.
Underlying Health Concerns: Conditions such as liver or kidney disease, hormonal imbalances, or use of specific medications.
Early diagnosis can prevent complications and help choose the most effective treatment plan.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia occurs when the glandular tissue in the male chest enlarges. Common causes include:
Hormonal Imbalance: An increase in estrogen relative to testosterone stimulates breast tissue growth.
Medications: Certain medications, including steroids, anti-androgens, and heart or psychiatric drugs, may contribute.
Obesity and Lifestyle Factors: Excess weight, alcohol use, and drug use can exacerbate the condition.
Medical Conditions: Liver disease, kidney disease, thyroid disorders, and hormone-producing tumors may trigger gynecomastia.
Identifying the cause is essential for determining whether medical management or surgical treatment is appropriate.
Medical vs Surgical Treatment
Medical (Non-Surgical) Treatment
Mild or early-stage gynecomastia may be managed without surgery through:
Lifestyle adjustments such as diet and exercise
Hormonal therapy if imbalances are detected
Adjustments in medications contributing to breast enlargement
Medical management is often effective in adolescents or adults with mild breast tissue enlargement.
Surgical Treatment
Persistent or severe gynecomastia may require surgery. Surgical options include:
Liposuction: Removes excess fat for a flatter chest.
Excision: Removes firm glandular tissue that cannot be treated with liposuction.
Combination Procedures: Often used for optimal results in moderate to severe cases.
Surgery provides permanent correction, restores chest contour, and boosts self-confidence.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery depends on the chosen treatment. Non-surgical interventions typically require minimal downtime, while surgical patients may need a few weeks to fully heal. Key aftercare steps include:
Wearing compression garments as advised
Avoiding strenuous activity until cleared
Attending follow-up appointments
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to prevent recurrence
Choosing the Right Clinic
Selecting a reputable clinic ensures safe and effective treatment. Look for experienced surgeons, comprehensive care plans, and modern facilities that prioritize both health and aesthetic outcomes. A thorough consultation helps patients understand the best approach for their condition and expectations.
Gynecomastia can affect appearance, comfort, and confidence, but timely medical attention can make all the difference. For professional evaluation, advanced treatment options, and expert guidance, patients rely on Enfield Royal Clinic in Islamabad for safe and effective gynecomastia care.